Location data has always been essential for businesses and consumers. The one advantage the modern world has today is that technology like LoRa Geolocation is on its side. The world has more data than before that it can rely on. On the flip side, there are solutions that can transform this info into actionable insights.
For instance, business leaders can use location data to track assets, map consumer movement in stores, and even make sense of their production processes. Governments can control vehicle movement and improve safety thanks to location data. There are many more use cases for location data, and LoRa geolocation technology happens to be among the flag-bearers of better location tracking. It allows stakeholders to calculate the location of people or assets to a granular level on a massive scale. Read on to learn more about LoRa geolocation data.
What Is Geolocation?
Geolocation refers to the exact location of a specific device. In most cases, it involves factoring in the longitudinal and latitudinal location of an internet-connected device, such as a tablet or cell phone. While geolocation won’t identify your specific location, it identifies the location of the device in use. Your specific location will only be identified if you are within the vicinity of the device.
In the industrial, manufacturing, health, and marketing world, geolocation can do wonders. These are fields that are increasingly requiring an easy way to find products, equipment, and personnel in real-time. For instance, a medical lab might need to know where specific patients are located within their facility.
When it comes to manufacturing, geolocation data can help prevent the collision of automated machines. Geolocation data can be leveraged for both indoor and outdoor purposes. It combines several network technologies that promote better location capabilities.
Understanding LoRa Geolocation
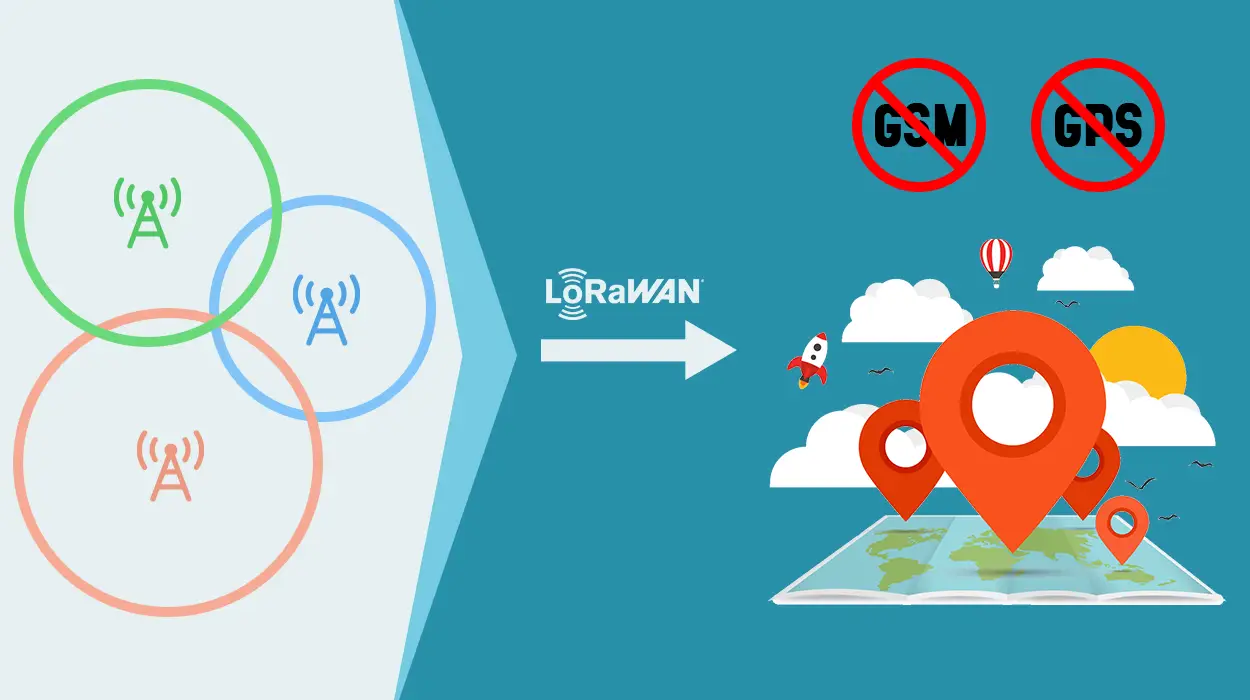
As a type of LPWAN (Low Power Wide-area Network), LoRa is meant to maximize power transmission range while limiting itself to lower power consumption. Also referred to as LoRaWANs (Long-range Wide-area Networks), the technology has proved to be quite efficient when it comes to geolocation services. It doesn’t rely on specific applications or consume a lot of power in comparison to Wi-Fi and GPS.
LoRaWAN can be classified into two parts. LoRa refers to the lower-level physical technology that modulates continuous radio signals with the help of discrete packets of bits. On the other hand, LoRaWAN is the name given to the higher-level abstract protocols that dictate the interactions between LoRa signals and gateways as well as encryption.
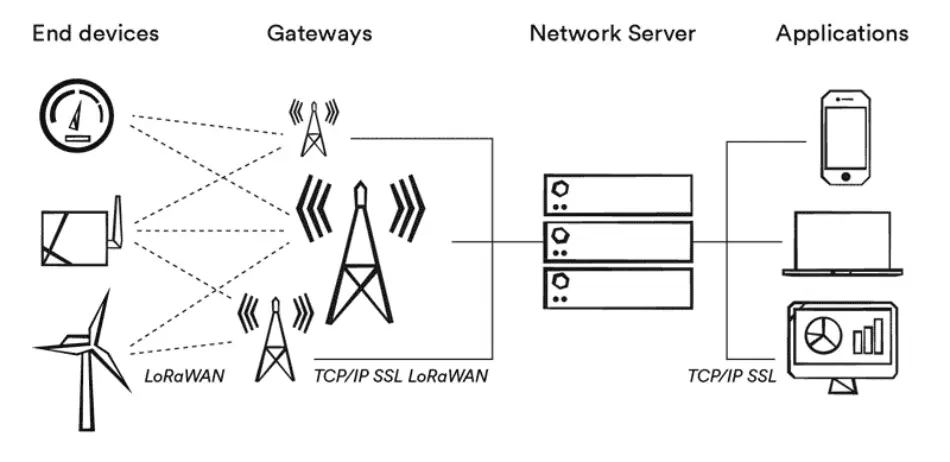
LoRa functions by sending periodic signals to gateways through specific nodes. The gateways allow you to configure them for communication with downstream nodes. This type of star topology is exactly what enables LoRaWANs to communicate over long ranges without consuming too much power.
LoRaWANs leverages Time Difference of Arrival (TDOA) or triangulation for geolocation. Essentially, a LoRa device can be located as long as three gateways interact with its signals. The gateways then calculate the device’s distance by factoring in the time the signal took to get to them. They can also factor in the extent to which the signal has dispersed. The former method is typically more reliable since the speed of light (which represents information transfer in this case) is continuous in a specific medium.
As long as you know the location of each gateway, identifying where the LoRa device is situated is quite easy. You simply need to draw a circle, whose radius is the identified device distance, around each gateway. The space where the three gateways’ circles overlap is the location of the device. The more gateways that are present, the more accurate the location of the devices will be.
Requirements For LoRa Geolocation
- A LoRaWAN gateway to receive data packets from nearby LoRaWAN devices
- A network server that will store the received signal-strength and signal-to-noise ratio for each antenna on every gateway receiving packets
- The location data (longitude, altitude, and latitude) of each antenna on every gateway that is receiving data from LoRaWAN devices
- An API token (key) to help with user authentication for each query
- Although optional, it can have accurate timestamps from every antenna on the LoRaWAN gateways
How to use LoRa Cloud Geolocation To Obtain Location Data
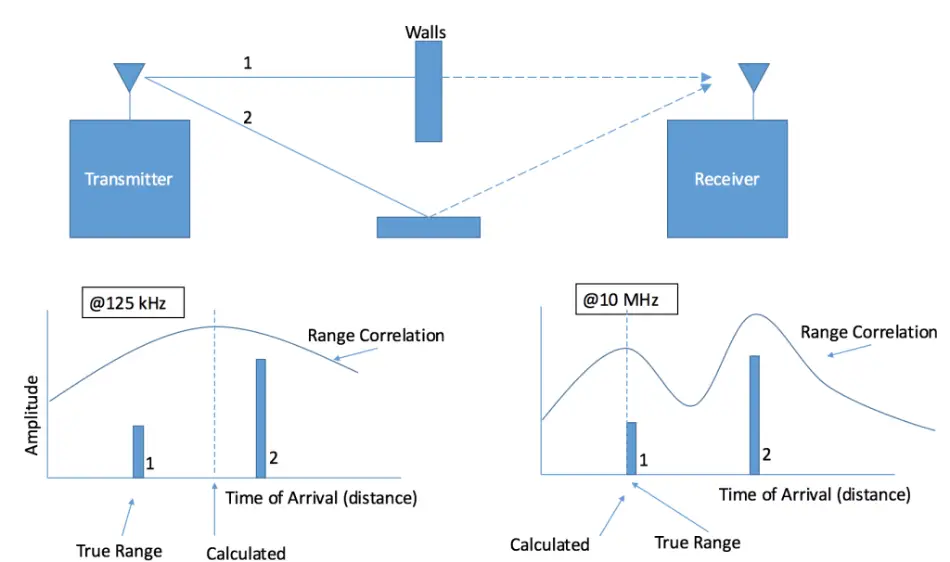
As long as they are within range, LoRaWAN gateways are designed to receive packets transferred by LoRaWAN devices. While there are cases where the packets will directly reach the gateway from the device, the packets have to bounce off buildings and other objects along the way. Some packets get to gateways through multiple paths The paths can be a combination of one or more reflected signals and those on a direct path.
The gateways then have to push the received packet to corresponding network servers. In case a single packet is transmitted to the server from multiple gateways, the server chooses to pick one copy and delete the rest. The only downside of this function is that while it is ideal for packet payload recovery, it doesn’t serve the geolocation purpose.
For optimal geolocation, all the metadata from every packet copy should be retained. In case the gateway has multiple antennae, the metadata from every copy of the packet needs to be retained.
LoRa Cloud Geolocation service functions under multiple algorithms for calculating location. The simplest option requires a signal-to-noise ratio and the signal strength for each copy of the packet. The geolocation service works with the help of a query, which mainly contains the signal-to-noise ratio, the signal strength, and the antenna location. Upon calculation, the service responds with the most likely device location based on the information on the query. In case the device sends multiple packets in the same location, the service can process all receptions for a more optimized location result.
Advantages Of LoRaWAN Geolocation
- Easy Deployment
Incorporating LoRa technology into your devices is quite easy and requires minimum effort. You won’t have to use special hardware, or additional Bill of Material (BOM) costs to have your devices work with LoRaWAN Geolocation services.
- Broad Applicability
LoRaWAN geolocation promises multiple applications. It can be used for asset management, retail store management, and even in logistics. In most cases, it can be a great alternative for use cases where GPS is battery-life-draining or cost-prohibitive.
- Simple And Secure
Over-the-air messages that are sent by LoRaWAN devices don’t contain any positioning information. They come with the standard 128 bits AES encryption, which prohibits the vulnerability of or unauthorized access to personal or asset geolocation information.
- Location Without Life Cycle Impact
Since the network-derived geolocation doesn’t require additional processing, it is easy to maintain LoRa’s low-power consumption aspect.
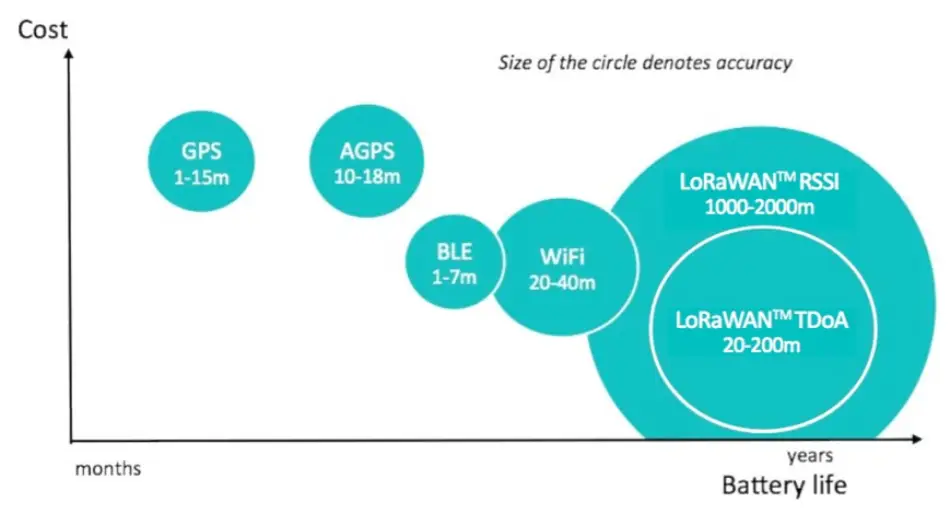
LoRa Geolocation Accuracy vs GPS vs AGPS vs BLE vs Wifi
Ideally, LoRaWAN geolocation accuracy spans between 20 meters and 200 meters. The accuracy is contingent on a few factors like the density of the LoRa network and the physical distance between devices and gateways. There is an inherent distance and accuracy tradeoff due to propagation errors. The denser the LoRa network, the more accurate geolocation will be, and the easier it will be to balance this tradeoff.
LoRaWAN geolocation accuracy is also affected by its surrounding physical environment. When used in large, flat, open areas, LoRaWAN has been seen to uphold high accuracy levels since there is less geographical or structural interference. On the other hand, it can be easy for accuracy to be affected by large structures and geographic variations in urban environments. As such, you will need a much denser LoRa device distribution in urban centers for similarly sized spaces.
In areas that are free from interference, LoRa has been observed to be as accurate as 3m. However, when interference takes center stage, like in urban areas, accuracy has been seen to range between 60 and 80 meters, as long as your account for timestamp and interference errors. This range might be ideal for identifying the general direction and location of an item.
Why Choose MokoLoRa Geolocation Solutions?
MOKOLoRa geolocation can be tailor-made to your specific needs. We observe high levels of quality to ensure every customer enjoys nothing short of the best outcomes. We stand out in many ways, including:
- Production for a global audience – you can get your LoRa devices delivered to you anywhere.
- A team of competent engineers – we nurtured our team over the years, with some accumulating decades of experience in the IoT and geolocation world.
- Professional testing – quality is essential to MOKO, which is why each product is taken through thorough tests to ensure it meets expectations.
- Tailor-made hardware – you can approach us with the specifications of your project, and we’ll create geolocation hardware that serves your intended purpose.
Our Solutions
We have a wide variety of solutions that can help you with your geolocation needs. They include:
- LoRaWAN GPS tracker
- LoRaWAN Module
- LoRaWAN gateway
- LoRaWAN T&H Sensor
- LoRaWAN Bluetooth Gateway
- LoRaWAN Panic Button
- LoRaWAN Parking Sensor
Applications Of LoRa Geolocation
- Asset Tracking Within Supply Chains
Knowing the specific location of shipments at all times is essential. Geolocation data can be used to identify the location of assets, atmospheric conditions of sensitive cargos, and even the direction of the shipment. This reduces theft and increases accountability.
- Help Find People Through Wearables
Finding staff members within your premises can be easier with LoRa geolocation. The technology can also come in handy when it comes to protecting seniors who are prone to falling. Medical professionals and their caregivers can use the geolocation data to find where they are at every moment to prevent fatal accidents.
- Vehicle Automation
For autonomous vehicles to move freely, they need to understand where they are at all times. LoRaWAN geolocation technology can be applied to the vehicles to showcase their exact location and prevent collisions with other vehicles.
- Building Smart Cities
Geolocation is made for smart cities that have inbuilt geographic intelligent systems. For instance, LoRa geolocation solutions can be used to geofence children and the elderly to prevent them from leaving a designated area. It can also be used for smart parking by informing each driver about free parking spaces.
- Agriculture
Geolocation can help promote smart agriculture. With LoRa geolocation technology, farmers can accurately map farm boundaries, irrigation systems, and roads. The technology is also great for precision planting and monitoring plant development over time.
LoRa Geolocation is the Future
LoRa Geolocation offers some great benefits over conventional location tracking technology. From being low-power-consuming to being able to track location over a wider range, it is exactly what the future needs. feel free to reach out to MOKOLoRa for insights on designing your LoRa device or to work with reputable manufacturers.