Over the past years, various technologies of the global Internet of Things have emerged one after another, especially in the field of low power wide area networks. The LPWAN market is dominated by NB-IoT and LoRa technologies, which support connectivity across industries and create innovative services such as smart gas and water metering and smart parking. The two technologies are often compared, and discussions about which is better for development are ongoing. This article tries to find out how businesses can choose between the two technologies to build the Internet of Things.
Trends and statistics: LoRa, NB-IoT and LPWAN
Despite the shortage of chipsets and the coronavirus pandemic, the global LPWAN market has seen significant growth in recent years. The market is expected to reach $46 billion by 2022 (up from just over $500 million in 2015). In fact, LPWAN has been a hot spot since 2016, with four technologies, LoRa, NB-IoT, Sigfox and LTE-M, accounting for more than 96% of the market share. More specifically, NB-IoT holds the leading share with 47%, followed by LoRa captures over a 36% market share.

The APAC region has been a big stage for LPWAN network technologies, and China is a critical market for the early adoption of and development of LoRa and NB-IoT. One of the key success factors of LoRa and NB-IoT is the support from the solid ecosystem of leading IoT vendors such as Amazon, Huawei, Qualcomm, and Cisco. Both major operators and equipment giants give customers a wider choice. It would be interesting to see what kind of support LoRa and NB-IoT will bring to the table when it comes to IoT deployment.
A brief introduction to LoRa and NB-IoT
NB-IoT and LoRa, as two of the most promising LPWAN communication technologies, com with different technical and commercial characteristics. These two technologies are designed with wide coverage, low power consumption, low cost, multiple connections, and low speed. Both of them are ideal for low power IoT applications and play an active role in expanding their ecosystems. Before delving into the comparison, let’s take a quick look at the two protocols.
What is LoRa
LoRa (Long Range) refers to an ultra-long-distance wireless transmission scheme based on spread spectrum technology, and is adopted and promoted by American Semtech company. It provides safe and two-way data transmission, and enables long-range communication with IoT networks for several years without battery replacement. It can send and receive signals up to 10 miles away, and if needed, the communication ranges can be extended to hundreds of miles through the use of repeaters.
By the way, pretty much people are wondering about the difference between LoRa and LoRaWAN. Although they are often mentioned synonymously, the two terms refer to totally different things. Specifically, LoRaWAN is an LPWAN protocol standard that operates in the LoRa technology environment. LoRa itself is a modulation method of the Internet of Things communication.
What is NB-IoT
NB-IoT (Narrow Band Internet of Things) is a technical standard defined by the 3GPP standardization organization to support a wide range of cellular devices and services. The specification was implemented in 3GPP Release 13 (LTE Advanced PRO) in June 2016. It mainly focuses on indoor coverage, low power consumption, low cost, and high connection density. The NB-IoT network has carrier-grade network standards and can provide better signal service quality, security and authentication, among others.
LoRa VS NB-IoT: a feature-by-feature comparison
If you search online, there are a lot of bits and pieces of information about the differences between LoRa and NB-IoT. The ABI Research even made a fantastic report on the comparison of the two technologies. The following section will show you a detailed comparison between LoRa and NB-IoT, and we will break down them from their similarities and differences.
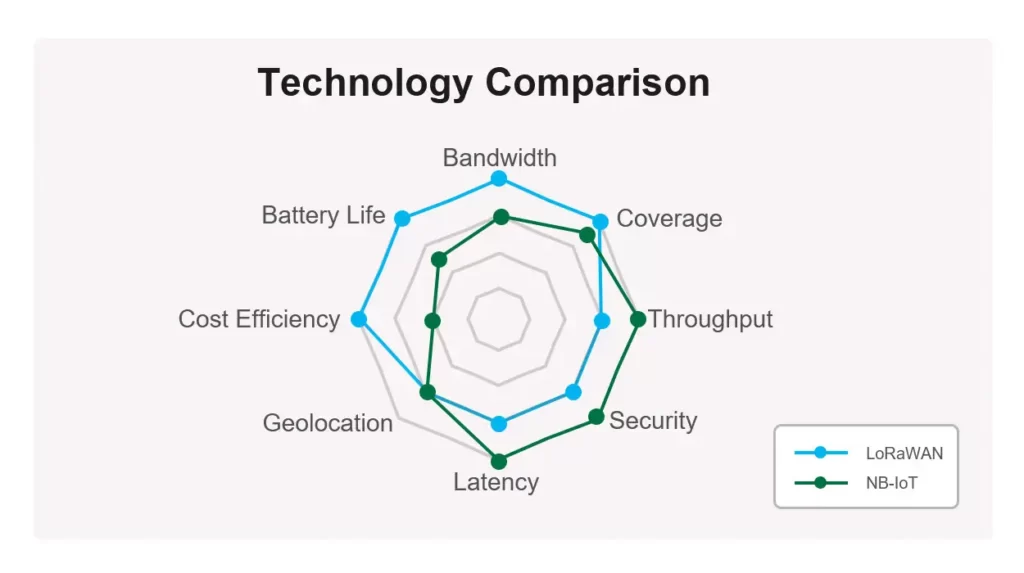
Similarities of LoRa and NB-IoT
- All belong to the new technology of IoT communication
NB-IoT was jointly launched by Huawei and China Mobile in 2016 and commercialized in 2017.
Lora technology officially launched LoRa Alliance in 2016 by Semtech and ZTE in the United States, and has been continuously promoted and developed in China.
- Supportwide coverage
Long-range communications are available to LoRa and NB-IoT to achieve wide coverage.
- Support low power consumption
Both NB-IoT and LoRa support low power consumption, with a standby power consumption of less than 10uA. And both support battery power and typically have an operational life in years.
Differences between LoRa and NB-IoT
- Networking
NB-IoT is based on cellular networking of mobile networks, while LoRa depends on the LoRa gateway. The terminal devices of NB-IoT can connect and communicate with the cloud directly. LoRa end nodes need to transmit the data to the gateway first, and then the gateway will communicate with the cloud platform.
Relatively speaking, the networking of NB-IoT is more convenient.
- Frequency band
LoRa operates in the unlicensed free ISM band, but it varies from country to country and region. The LoRa Alliance devotes itself to promoting the standardized LoRaWAN protocol globally, enabling devices that conform to the LoRaWAN specification to be interconnected.
NB-IoT uses licensed frequency band and can be deployed in 3 ways: stand-alone, guard-band, and in-band. Most of the operators worldwide utilize the 900 MHz for NB-IoT, with some deploying in the 800 MHz. NB-IoT belongs to the licensed frequency band, which, like 2G/3G/4G, is a specially planned frequency band with relatively little interference. Moreover, it can be integrated with the existing cellular network base stations.
The cost of band licensing is not cheap these days – more than $500 per MHz.
- Transmission distance
Long range coverage is what both LoRa and NB-IoT have in common, but NB-IoT performs better with an extending coverage up to 18 – 20 km, which is higher than the 12 – 15 km supported by LoRa.
An interesting fact worth noting, however, is that NB-IoT works well in cities, but its performance is average in suburbs or rural areas (anywhere without strong cellular coverage). The coverage of LoRa across all regions remains relatively stable since it does not rely on cellular data or WiFi.
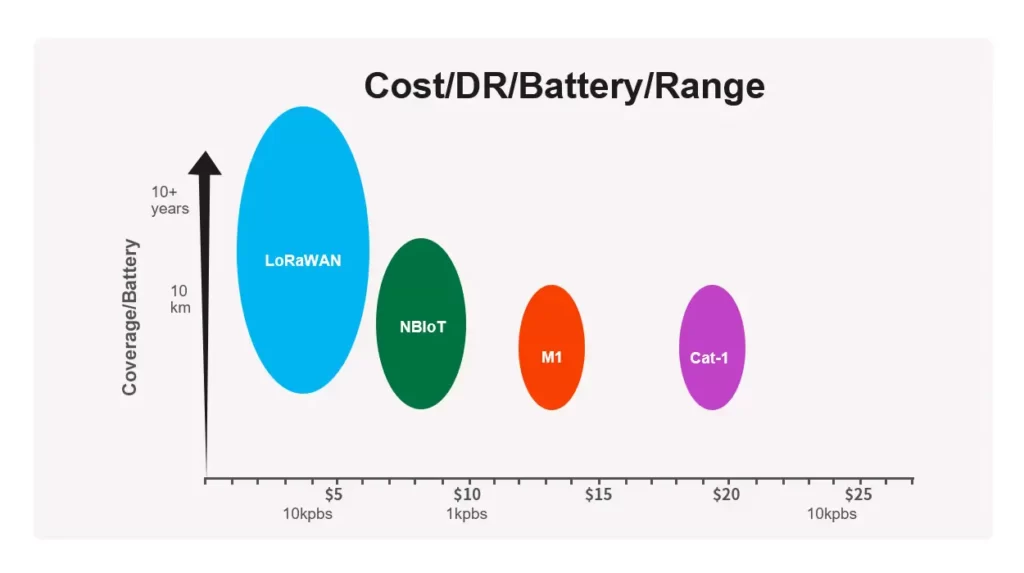
- Battery performance
LoRaWAN performs better in this regard. As NB-IoT operates in cellular licensed spectrum, devices must synchronize to the network periodically and frequently, which in turn consumes power. However, no such network synchronization is needed in the ALOHA-based LoRa architecture.
The LoRa end application can precisely determine the ‘sleep’ time of the device, so battery power can be easily conserved. The linear transmitter of NB-IoT requires several orders of magnitude more ‘peak current’ than LoRa with nonlinear modulation, which puts additional strain on the battery.
- Data transfer rate
The data rate of B-IoT communication can theoretically reach 160Kbp-250Kbps, while the communication rate of Lora is about 0.3-50Kbps. In this respect, NB-IoT can throw LoRa out of the game.
The higher data rates of NB-IoT make it perfect for applications that demand faster data throughput.
- Number of supported nodes
In theory, a single NB-IoT base station can support 200,000 nodes, while LoRaWAN supports more than 60,000.
- Cost
On matter how powerful LPWAN protocols are, the operating cost is a critical factor to consider, otherwise, they are unlikely to be viable IoT solutions. LoRa has an advantage here. The total cost of LoRaWAN modules is about $8 – $10, which is about half the price of NB-IoT modules.
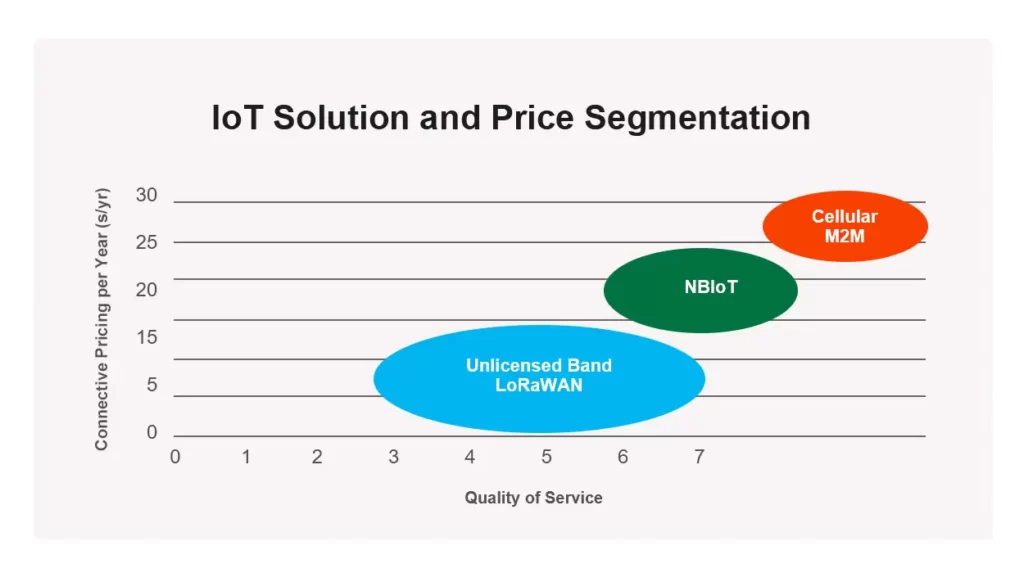
The more complex the deployment of the NB-IoT network, the higher the IP related cost (in terms of licensed spectrum), thus increasing the overall cost of NB-IoT. It is more expensive to upgrade NB-IoT to advanced 4G/5G/LTE base stations than deploy LoRa via industrial tower-top gateways. The cost of LoRa technology is expected to witness a further decline as the market matures.
- Private network capability
The market for LoRaWAN technology has gradually matured and gained wide popularity in public networks. It has been deployed across the world to build ‘smart cities’. Though NB-IoT gains great acceptance in the public domain, it is not as applicable as LoRa in the private networks of enterprises.
Moreover, large businesses can take advantage of LoRa to create hybrid IoT models to build intelligent facilities, and at the same time, they can utilize public networks to process off-device information and activities. Note that NB-IoT is only available in public network mode.
A comparison chart of NB-IoT VS LoRa
| LoRa | NB-IoT | |
|---|---|---|
| Year of development | 2015 | 2017 |
| Frequency band | Unlicensed spectrum | Licensed frequency bands |
| Transmission coverage | 12 - 15 km | 18 - 20 km |
| Number of supported nodes | 60,000 | 200,000 |
| Data transfer rate | Lower data transfer rate | Higher data transfer rate (10x LoRa’s rates) |
| Battery performance | Longer battery life | Shorter battery life |
| Cost | Lower cost per device (but gateway required) | Higher cost per device (but no gateway required) |
| Private network capability | Yes | No |
Different use cases of LoRa and NB IoT
When it comes to the application, NB-IoT and LoRa maintain a competitive and complementary relationship. In areas such as smart metering where you can adopt both LoRa and NB-IoT, they are competitors. The NB-IoT network is more suitable for terminals with a wide range of activities, and LoRa technology is ideal for underground and remote areas where NB-IoT network is unstable.
NB-IoT applications
- Sharing bikes: Wide distribution and low unit density, making it suitable for operator networks.
- Smart metering: Water meters, electricity meters, gas meters, etc. There are low requirements for acquisition frequency and network availability, and self-built base stations are out of consideration.
- Smart wearable: Terminal devices are distributed in the whole urban area, which is perfect for operator networks.
- Smart logistics: Positioning terminals are moving across regions, and the interval frequency of uploading is not high.
- Water/pipe network monitoring: Wide distribution and small unit density.
- Smart parking: The change of magnetic field is induced by geomagnetic field to determine the parking space of vehicles.
LoRa applications
- Smart metering: Users have high requirements on collection frequency, data analysis and network availability.
- Smart parking detection: Certain requirements in collection frequency and terminal devices life.
- Suburban: Such as mining, extractive industries, and heavy industries.
- Closed areas: Users in universities, parks, and buildings want to build private networks to manage their own applications and facilities.
- Industrial data transmission: Strong anti-interference, long transmission distance and stable data transmission are required.
LoRa or NB IoT – Competitors or Complementary?
You may find that many technical articles compare LoRa and NB-IoT technologies as if they are fighting over who dominates the IoT market. In fact, as two emerging technologies, LoRa and NB-IoT standards were designed to enhance the power efficiency, security and interoperability of IoT devices. Overall, each of them has its own strengths and weaknesses to cater to different target user groups. The choice of technology depends on the needs of users, and it should be chosen reasonably according to your actual project.
Both NB-IoT and LoRa are still in their early stage of development and require investment and joint efforts from all parties. When large-scale implementation becomes possible, the deployment cost of NB-IoT and LoRa will naturally be further reduced. In this new wave of IoT development, the implementation of project should be a priority in order to obtain competitive advantages. Product innovation is necessary for LoRa and NB-IoT, and project application innovation should be put under great emphasis. It’s hard to say who will win the match, after all, everything is possible.